
Evaluation of the role of kras gene in colon cancer pathway using string and Cytoscape software
- Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Science, Lincoln University College, 47301 Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia
Abstract
Introduction: cancer is one of the top three most commonly occurring cancer worldwide with more than 1.8 million cases in 2018. In Malaysia, cancer is the most common cancer in males and the second most common cancer in females. Albeit being the second most common form of cancer in Malaysia, there is a lack of informal or structured national cancer screening program in Malaysia and it remains a low priority in healthcare planning and expenditure. The risk of developing colon cancer is greatly influenced by factors such as lifestyle habits, genetic inheritance, diet, weight, and exercise. KRAS, the most frequently mutated oncogene in cancer, occurs in about 50 percent of cancers. This study maps the KRAS gene involved in colon cancer pathway using applications such as STRING version 11.0 and version 3.7.0 to provide a clear visualization of all the related and involved proteins and genes that interact with KRAS gene in the pathway. Methods: Using KRAS as a seed, a protein-protein interaction network was constructed with 3391 interactions which were retrieved from the STRING version 11.0 database. The protein network interaction was further grouped into 6 clusters using the MCODE application. Molecular function and biological processes of the genes involved in the KRAS protein network were determined using Biological Networks Gene Ontology (BiNGO). Results: According to the resulting protein-protein network interaction map, it revealed that KRAS mechanism and co-expressed genes interconnected with protein or enzyme binding, receptor signaling protein activity and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2 binding. Conclusion: Understanding these protein-protein interactions provide insight into cellular activities and thus aid in the understanding of the cause of disease.Introduction
Globally, the incidence and mortality of cancer are increasing rapidly. Statistically, colon cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide for both men and women1. Most colon cancers are classified as adenocarcinomas which are subdivided into low and high grades based on the type of tumor1. Both environmental and genetic factors influence the risk of colon cancer. Such risk factors include age, diet, family history, cigarette smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption.
In Malaysia, males are mostly affected by colon cancer. On top of that, the exact cause of colon cancer remains unknown to date. It is because most of the cases occur occasionally, although 20-30% of the patients do have a family history of colon cancer1. Besides, there are a few risk factors that can cause colon cancer. For example, increasing age and diets high in fat may lead to colon cancer.
The genetic alterations in colon cancer include chromosomal instability, microsatellite instability, and aberrant DNA methylation2. These are inheritable changes that affect an individual in different ways. Chromosomal instability occurs due to the alteration in the number of chromosomes. It leads to the inactivity of tumor suppressor genes such as APC (adenomatous polyposis coli), p53 (tumor suppressor p53), and SMAD42. Microsatellite instability occurs when the DNA mismatch repair does not function properly. In this case, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 genes undergo mutation which initiates colon cancer2. On the other hand, aberrant DNA methylation is the abnormal process of DNA methylation that leads to the formation of tumor. Besides, the activity of oncogenes such as Ras, EGFR (ErbB-1), ErbB-2, TGF-alpha, and TGF-beta-1 is also associated with colon cancer2.
The KRAS gene regulates important cellular signaling pathways such as PI3K and MAPK pathways. A mutation of the KRAS gene results in hyperplasia. However, when it is coupled with APC mutation, an adenoma can progress to cancer3. In this study, KRAS gene related to colorectal cancer pathway was mapped using STRING and Cytoscape software to learn about the alterations modulating the functioning of associated genes in the colorectal cancer pathway.
MATERIALS – METHODS
Determination of genes participated in KRAS pathway
Software that was suitable and compatible according to what was required for this study was chosen. On the STRING version 11.0 (Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes, available at https://string-db.org/) webpage, KRAS was typed into the search box for protein name and the organism field was set to . The closest match for the search query was chosen in the results section. Once the map was created, desired parameters such as interaction sources, interaction scores, and clustering were adjusted. This showed the KRAS protein network and its interactions with other proteins. The network was further grown to obtain 200 interactors to make it more manageable to analyze. The prediction methods selected for this analysis included Neighborhood, Gene Fusion, Co-occurrence, Co-expression, Experiments, Databases, Protein Homology, and Text Mining. The protein interaction network was adjusted to only those interactions which had a confidence score higher than 0.9, representing greater than 80-90 % confidence level in the predictions. This bioinformatics tool was chosen as it offers many advantages. These included consisting of an extensive collection of pre-computed interaction data derived from varied sources (such as high-throughput experimental data, literature data, and computational predictions), scoring of the network interactions using probabilistic scoring to obtain higher confidence in the interactions, and allowing grouping of interacting molecules into clusters using the advanced mode algorithms Markov clustering (MCL) and K-Means.
Clustering of KRAS gene analysis using Cytoscape
Cytoscape version 3.7.0 (an open source software platform for visualizing networks) was downloaded. The KRAS interaction network obtained from STRING was opened on Cytoscape. From the results page of the molecular networking, the graphML file was downloaded for Cytoscape. From the Toolbar, File / Import / Network / File (or cmd + L) were selected, and then the graphML file was selected in the root of the unzipped job folder. After that, a new Cytoscape style was generated for node styling and node label to spectrum property. Using this software, the network interaction was further grouped into clusters using the MCODE application, which groups molecules based on pre-specified criteria. A cluster is a set of objects which share some common characteristics. The existing network was grouped into 6 non-overlapping clusters. The information related to the protein molecule, interaction type, and source of interaction were retrieved by the STRING database. The protein interaction network was presented using Cytoscape software. Clustering in protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks therefore includes identifying protein complexes and functional modules. This process is useful in clarifying the PPI network structures and their components of inter-relationship, inferring the principal function of each cluster from the functions of its members, and interpreting the possible functions of members in a cluster through comparison with functions of other members.
Functional gene analysis using BiNGO
The function of each related genes in colorectal cancer was identified with the help of the Biological Networks Gene Ontology (BiNGO) application. The biological functions and molecular mechanisms of each cluster were identified using BiNGO analysis.
RESULTS
Using KRAS as the seed, a total of 500 interacting proteins with 3391 interactions were constructed using the STRING version 11.0 database. The interactions based only on text mining were verified using the PubMed literature database. The result of the protein-protein interaction network is a highly connected network of molecules (Figure 1). The protein interaction network is visualized in the form of a graph network, with the protein molecules forming the nodes of the graph and the interactions forming the edges. Most of the proteins are at the center of the network with few molecules loosely arranged at the periphery. Some interactors are connected by multiple lines which indicate interactions that are derived from more than one source of information.
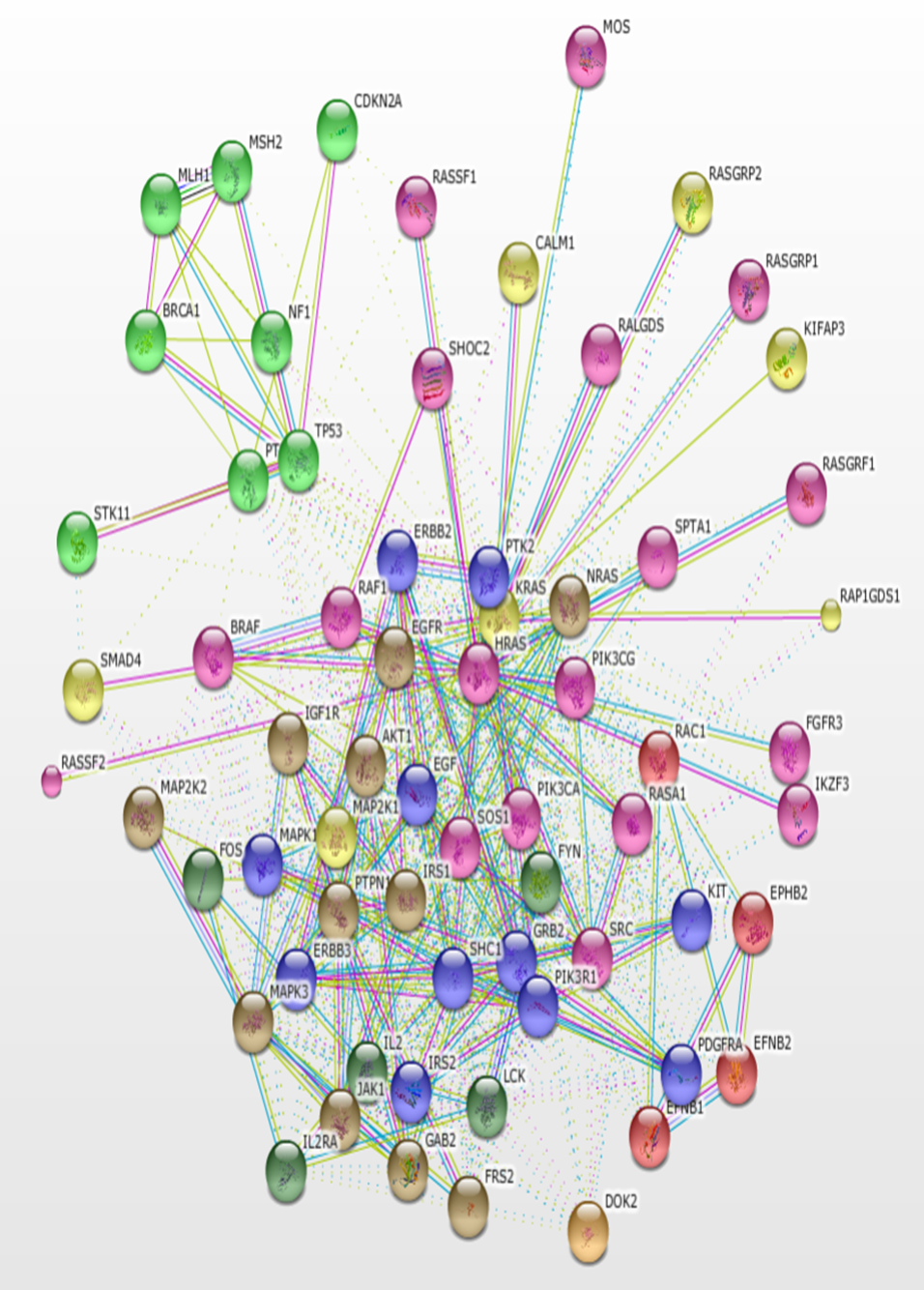
Using KRAS as seed, a total of 500 interacting proteins with 3391 interactions were constructed using the STRING version 11.0 database.
The protein network interaction was further grouped into 6 clusters using the MCODE application (Figure 2). Each cluster was then analyzed and the information of the genes involved in that particular cluster, score, nodes, and edges were gathered (
Related genes in eachof the 6 clusters mapped using Cytoscape
| Cluster | Score | Nodes | Edges | Genes |
| 1 | 41 | 41 | 820 | RAP1B, YWHAB, HRAS, FGA, FAM131B, KIAA1549, MAPK3, KRAS, APBB1IP, NRAS, PEBP1, CSK, ARAF, BCL2L11, CNKSR2, ESRP1, TRIM24, LMNA, ARRB2, ITGB3, ATG7, SRC, AP3B1, SND1, MAPK1, MAP2K2, KSR2, FXR1, QKI, ARRB1, BRAF, MAP2K1, FN1, RAP1A, IQGAP1, CNKSR1, VWF, KSR1, RAF1, VCL, TLN1 |
| 2 | 12.784 | 52 | 326 | IL5, IL3, YWHAZ, CSF2, GAB2, FGF9, PPP2R5E, ERBB2, YWHAG, NRG1, FGFR2, FGF1, YWHAQ, YWHAH, FYN, IRS1, FGF6, SFN, NRG3, FRS2, YWHAE, IRS2, EREG, FGF19, FGF7, PDGFRB, PDGFB, FGFR4, FGF20, FGF16, FGFR3, PRKCZ, PPP2R5A, HBEGF, FGF10, NRG2, JAK3, JAK1, UBB, UBC, FGF2, FGFR1, PIK3CD, CDC37, HSP90AA1, FGF3, EGF, EGFR, IL2, IL2RA, BTC, FGF4 |
| 3 | 8.235 | 35 | 140 | CAMK2D, GRIN2A, CAMK2B, RASAL1, RASGRF2, PAK1, DAB2IP, RASGRF1, SHC1, GRIN1, NTF4, SPRED1, CAMK2A, SOS1, PIK3R1, DLG4, GRIN2B, NTRK3, PAK2, NF1, SYNGAP1, PRKCD, RASAL3, PPP2R1A, IGF1R, RASA3, RASA2, PTPN11, CAMK2G, PPP2CA, SPRED2, RET, GDNF, RASA4, RASAL2 |
| 4 | 7.909 | 23 | 87 | NTF3, TP53, ERBB3, PTK2, RAC1, RHOA, PPP2CB, YES1, PIK3CB, PPP2R1B, PDGFRA, BDNF, NTRK2, PRKCA, HGF, PPP2R5C, MET, GRB2, LCK, MAPK8, LYN, KIT, MLLT4 |
| 5 | 3.75 | 9 | 15 | NFKB1, EPHB2, TEK, ANGPT1, TIAM1, PRKCB, PRKCE, PIK3CA, RELA |
| 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | NCAM1, PTPRA, SPTA1 |
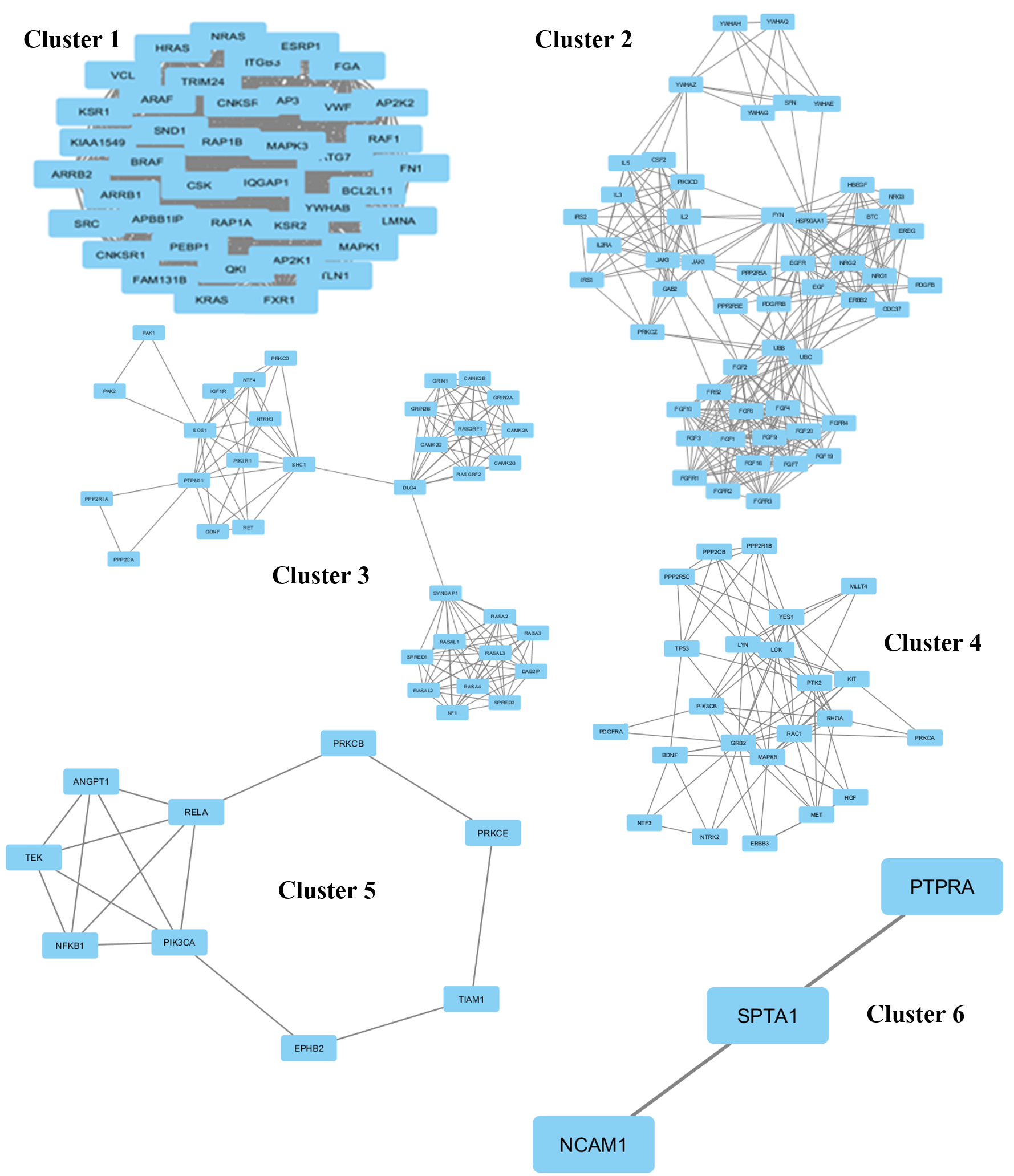
Six specific non-overlapping clusters of various sizes, which emerged from the huge network of protein-interactors, were determined using K-Means clustering algorithm.
Then, the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of each cluster were identified using BiNGO analysis, which is one of the plugins in the Cytoscape version 2.7.0 software.
DISCUSSION
Upon analysis, various data were obtained:
(i) In the first cluster, there are 41 highly connected proteins that serve as interactors, including KRAS which was found to be highly connected, interacting with many proteins. This dense cluster consists mostly of proteins that are involved in binding and kinase activity. The proteins are mainly involved in protein binding, enzyme binding, receptor signaling protein activity, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding, angiotensin receptor binding, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding. Some proteins in this cluster, such as ARRB1, KRAS, ARRB2 and MAPK3, are involved in transcriptional activity.
(ii) The second cluster consists of 52 interacting proteins, most of which are involved in kinase activity, including IRS1, PDGFRB, ERBB2 and PIK3CD. Most of the remaining proteins are also involved in kinase and growth factor activities; these include fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), and fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9). Besides that, some of the proteins have participated in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor binding, interleukin-3 receptor binding, kappa-type opioid receptor binding, protein kinase C binding, platelet-activating factor receptor activity, and heat shock protein binding.
(iii) In the third cluster, 35 interacting proteins are distantly related, whereby the proteins are only directly related to 3 proteins, which are SHC1, DLG4 and SYNGAP1. SHC1 is important in the regulation of apoptosis and drug resistance in . Its over-expression is associated with cancer mitogenesis, carcinogenesis and metastasis. DLG4 encodes the protein SAP-90, also known as synapse-associated protein 90, and is involved in anchoring synaptic proteins. SYNGAP1 codes for the protein SynGAP which is important in nerve cells in the brain. This cluster is mostly related to binding and kinase activity. Some of the proteins are involved in stem cell factor receptor binding, ligand-gated ion channel activity, calcium channel activity, dopamine activity, and neurotransmitter binding.
(iv) In cluster four, there are 23 interacting proteins and many of those are involved in binding and kinase signaling. In this cluster, TP53 is actively involved in the activity of DNA strand annealing.
(v) The fifth cluster is an interaction of 9 proteins. These 9 proteins consist of those involved in transcription (transcription repressor and activator), kinase activity, and binding. TIAM1, PRKCE, TEK and EPHB2 are involved in signal transducer activity.
(vi) In the sixth cluster, there are three proteins (PTPRA, SPTA1 and NCAM1). PTRA is involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.
KRAS mutation occurs in approximately 50 % of colorectal cancers. KRAS is a member of the oncogene family. This oncogene is located at 12p which refers to the short arm of chromosome 12. The protein produced by KRAS gene, the KRAS protein (also known as p21), is part of a signaling pathway known as the RAS/MAPK pathway. KRAS usually functions in signal transduction cascades initiated by the binding of EGFR, hepatocyte growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor to their receptors. This protein couples with a cytoplasmic GTPase via the process hydrolysis. This GTPase regulates cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and migration. When this KRAS protein couples with GTPase, it converts guanosine triphosphate into guanosine diphosphate which modifies transductive signals from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. This, in turn, controls the cellular growth and its survival pathways. When KRAS is activated, it activates over 20 known downstream effectors, including Raf, Braf, mTOR, MEK1 and 2, ERK, AKT, and PIK3CA. These downstream effectors exert many different effects, including apoptosis suppression, promotion of cell growth, cell transformation, angiogenesis, migration, and differentiation. However, when the KRAS gene is mutated, guanosine triphosphate is maintained instead of being converted into guanosine diphosphate, which results in the signal being persistently on. For it to be able to turn off the signal, the binding of guanosine triphosphate to KRAS has to occur.
KRAS mutations usually result in a single amino acid substitution at one of three codons, namely codon 12, codon 13, or codon 61. Approximately 80 % of mutations occur in codon 12, and 15 % occur in codon 13. Codon 12 usually encodes for glycine. A mutation in this codon results in the replacement of a glycine with an amino acid which chemically interferes with the guanosine triphosphate hydrolysis process. This causes independent intracellular signaling and the cell permanently stimulates proliferation and the evasion of apoptosis. Conversely, a mutation on codon 61 disrupts the coordination of a water molecule which is required for GTP hydrolysis. These disruptions induce tumor development.
Activated KRAS regulates multiple cellular functions through well-described effectors such as the Raf mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase (MEK)/-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. MEK is frequently activated in human colorectal tumors. KRAS is also linked to nuclear factor NF-kB, a transcription factor that regulates inflammatory and immune responses and cell survival. Among the genes found to be involved in colorectal cancer are MSH2 and MSH6 (both on chromosome 2), MLH1 (on chromosome 3), PMS2 and EPCAM. Mutations in any one of these genes are enough to cause Lynch syndrome.
As analyzed in this study, protein-protein interactions play an essential role in various biological processes such as the cell cycle, metabolic pathways, and signal transduction. Understanding the protein-protein interaction is very crucial as it can give insight into the regulation of cellular activities. The studies on protein functional interactions can be further extrapolated to genes which could further help in the understanding of the etiology of a particular disease. Genes that lie in the neighborhood of a disease-causing gene in that network are more likely to be associated with the same disease. Novel disease genes have been identified by studying the protein-protein interaction network, and proteins that are involved in cancer are highly interconnected. Studies on protein-protein interactions in colorectal cancer have helped in determining pathways that are altered in the regulation of cancer stem cells.
Understanding the biological networking of KRAS is important in studying the KRAS pathway in colorectal cancer. KRAS mutational status is a critical factor when considering the use of targeted therapies. Different mutation locations produce different types of tumors; for instance, a mutation of codon 12 is associated with mucinous colorectal carcinoma while a codon 13 mutation results in non-mucinous cancers, but with increased aggressiveness and increased metastatic potential. The latter also occurs with increased frequency in metastatic lymph nodes.
A computational approach has been applied in this study to retrieve and analyze the interactions of KRAS protein through the use of STRING database as it allows for the feasibility of understanding the interactome using data from multiple sources. The STRING database was used in this analysis for mining protein interactions as it displays interactions that are based not only on verified experimental sources but it also predicts interactions based on text mining. This provides a wider base for analyzing the protein interactome. KRAS was used as a seed to discover information regarding its interactions with other proteins and to identify other proteins that might be involved in colorectal cancer along with this gene. The output interaction network that was obtained from STRING is represented as a connected network of molecules where the edge represents interactions between the molecules. The analysis of the proteins involved in colorectal cancer helps in understanding the pathways in this disease and identifies critical targets for drug therapy. Through this analysis, it is observed that the disease proteins play an important role in the tumorigenic sustenance process. Examining the expression of the molecules which interact with the disease proteins can help to identify new pathways of disease pathogenesis.
Mishra 20114 study demonstrated the importance of the KRAS and CDKN2A genes by linking them with 21 other neighbor genes, including PIK3CA and TP53, using the merged profile network. The protein-protein interactions showed a major variation in their expression pattern. The study also reported the importance of changes in KRAS, CDKN2A andTP53expression levels in pancreatic cancer cells. These results will aid in detecting the disease at the early stages and finding potential cures.
Zhang and his colleagues (2018)5 analyzed the EGFR-targeted drug genes that worked efficiently against KRAS wild-type and KRAS mutations in colorectal cancer. They carried out gene expression analysis and found 294 genes upregulated in KRAS wild-type and KRAS mutated samples. They used collagen type I α1 (COL1A1) as a seed in the STRING network and identified its interconnected genes that were responsible for colorectal cancer. Then, they exported the data from STRING to Cystoscope analysis to find the important network, biological functions, and molecular functions of the genes. They found that the results obtained from the web-based data-mining platform were consistent with a cancer microassay database (Oncomine). The results show that COL1A1 was significantly upregulated in KRAS wild-type and KRAS mutation samples of colorectal cancer.
Cao and his group (2019)6 investigated the prognostic significance of Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 (BIRC5) in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) lacking EGFR, KRAS, and ALK mutations (triple-negative (TN) adenocarcinomas). They used BIRC5 as a candidate and predicted its mechanism by a co-expressed network and gene set enrichment analysis. The protein-protein interaction network was constructed by Cytoscape. The gene set enrichment analysis determined the ontology function of the genes. The cluster groups were generated using the MCODE algorithm. A total of 159 genes were identified from Cytoscape. Nine cluster groups of genes were extracted using MCODE. The molecular functions and biological activities of the genes were determined. They found that the mechanism of BIRC5 and co-expressed genes may be linked with the cell cycle. Thus, BIRC5 is a potential predictor and therapeutic target (via controlling the cell cycle) in TN adenocarcinoma.
In this study, it reported that KRAS was mainly involved in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2 binding. Therefore, this information will aid in designing VEGF-targeted drug genes that work against KRAS in colorectal cancer. Furthermore, KRAS mechanisms and co-expressed genes interconnected with protein or enzyme binding and receptor signaling protein activity. With a comprehensive understanding of the binding of the substrate to enzyme, substrate-based drug design (SBDD) can provide an opportunity to target allosteric site sites, thus expanding the possible pathway to modulate the functions of the targets.
Alterations of genes in the KRAS pathway might disrupt the pathway and might be significant contributors to block the tumorigenesis process of colorectal cancer. For example, the blockade of the cell cycle and PI3K-AKT signaling may impact lung and head and neck squamous cell cancer; moreover, inhibition of PARP and AURKA can cause the inactivation of BRCA1 or BRCA2 in breast and ovarian cancers, preventing the proliferation of cancer cells and inducing abnormal cells to undergo apoptosis.
Conclusion
In this study, a total of 500 genes with 3391 interactions were identified using the STRING version 11.0 database. KRAS gene was used as a seed for this protein network construction. The protein network interaction was further grouped into 6 clusters using the MCODE application. Furthermore, KRAS mechanism and co-expressed genes interconnected with protein or enzyme binding, receptor signaling protein activity, and VEGF receptor 2 binding.
The proteins functionally interacted with each other; therefore, alteration of protein or enzyme binding and modulation of the signaling pathway might disrupt the expression of interacting proteins and lead to the blockade of cancer pathogenesis. Moreover, this study observed the interactions of KRAS and its neighboring, interacting proteins with the help of bioinformatics applications which predict protein-protein interactions and looks for differences in the network among the different clusters. These information form a basic understanding of malignancies. Thus, this approach can be useful in identifying better prognostic markers and therapeutic strategies for colorectal cancer.
Abbreviations
APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli
BiNGO: Biological Networks Gene Ontology
BIRC 5: Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5
COL1A1: Collagen type I α1
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor
FGF 2: Fibroblast growth factor 2
MCL: Markov clustering
p53: Tumor suppressor p53
PPI: Protein-protein interaction
SBDD: Substrate-based drug design
STRING: Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes
VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Science, Lincoln University College, Malaysia.
Author’s contributions
SMPM performed the experiments, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. AE suggested the idea, explained the data, corrected the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

