
The APC gene rs41115 polymorphism is associated with survival in Iranian colorectal cancer patients
- Liver and Gastrointestinal Diseases Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
- Midwest Biomedical Research Foundation, Kansas City, MO, USA
- Hematology and Oncology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Abstract
Introduction: The onset of colorectal cancer is a complex process caused by numerous genetic pathways. APC functions as a ``"gatekeeper" and its mutations occur at the initiation stage of the colorectal tumorigenesis. The main aim of this study was to investigate common somatic mutations of exon 15 APC genes in patients with colorectal cancer in East Azerbaijan, Iran.
Methods: This study was designed and performed as a cross-sectional and case-only study. Tissue biopsies were obtained during colonoscopy and confirmed colorectal carcinoma cases were evaluated. Two hotspot regions of exon 15 for APC mutations were evaluated using PCR amplification and Sanger sequence analysis.
Results: The synonymous (p.Thr1475Thr) polymorphism was observed in all patients; 35 patients (61.4%) had AG genotype and 22 patients (38.6%) had AA genotype. Also, a missense mutation and two deletions were found. Pearson's correlation test showed a significant correlation between the stage of the disease (rho = 0.23, P =< 0.05), and anatomical subsite of the tumor with rs41115 polymorphism (rho = 0.31, P =< 0.05). Overall comparison of survival function in the different genotypes of the APC gene showed significant differences between groups, and CRCs with AG genotype had 3.24-fold higher hazard of mortality than CRCs with AA genotype (HR = 3.24; 95% CI: 1.21 - 8.68, P = 0.020).
Conclusion: APC mutation plays an important predictive role in overall survival. However, the pattern and type of APC gene have a diverse impact on clinical outcomes in the Asian population. Moreover, in CRC patients the APC mutations were reported to be diverse variants.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC), one of the most prevalent types of cancer, has become a major health problem worldwide. Globally CRC is the third leading cause of death, with more than 1.8 million new cases and 800,000 deaths registered each year1. Recently, CRC has become the third most common cause of cancer in males and the second most common in females in Iran2. In the East Azerbaijan Province (Northwest of Iran), there are high incidence rates of mostly gastrointestinal cancers, with CRC as the second most common cancer in both sexes and with an increasing trend in age standardized incidence rates during the last decade3, 4, 5.
About 70-80% of colorectal cancers arise as sporadic form; only 5 - 10% of germline mutations lead to hereditary colorectal cancer6. Sporadic CRC occurs in old age and is most common after the age of 507. The onset of colorectal cancer is a complex process caused by numerous mechanisms including three major genetic pathways: Chromosomal Instability () Pathway, CPG Island Methylator Phenotype (), and Microsatellite Instability () Pathway8, 9.
Tumor suppressor genes (such as , ), oncogenes (such as (catenin protein encoder), and ), and encoding repair system genes (such as and ) are genetic factors that play a role in the development of colorectal cancer by different mechanisms10. The gene spans about 100 kb of genomic DNA, has a coding region of 8,532 base pairs, is located on chromosome 5q21-22, and contains 21 exons. Exon 15 is the largest exon covering over 75% of the coding sequence of . The gene encodes a 312- protein that performs diverse cellular functions such as microtubule stability, cell-cell interaction, cell polarity, cell migration and apoptosis11, 12, 13.
The protein has several domains in its structure through which it interacts with various proteins, and this reflects the different functions. The protein exerts its main role in the signal transmission pathway and is a regulator of the cell cycle. functions as a “gatekeeper” and its mutations occur at the initiation stage of colorectal tumorigenesis14. Mutations in the gene are often frame-shifts, insertions, or deletions which introduce premature stop codons and lead to the production of a truncated protein15. The mutant form of is found in both sporadic and inherited colorectal cancer as nonsense point mutation or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)16. However, 60% of all mutations that occur in the gene (45 - 35% of all sporadic colon tumors) are in the MCR region of Exon 15, with this region containing about 10% of the protein coding sequence.
The main aim of this study was to investigate common somatic mutations of exon 15 gene in patients with colorectal cancer in East Azerbaijan (located in Northwest of Iran), known to have the highest Azeri Ethnic population. In addition, the aims are to assess any clinicopathological aspects with mutation patterns of , as well as to evaluate their prognostic impact in CRC.
Materials and Methods
Patients
This study was designed and performed as a cross-sectional and case-only study, with 60 colorectal cancer patients recruited in East Azerbaijan during 2019. Tissue samples were obtained by tumor tissue biopsies during colonoscopy and were evaluated after pathologic confirmation of colorectal carcinoma. All patients signed informed consent to participate in the study. Pathology reports were used to confirm the diagnosis, with all available cytology, histology, necropsy and immunohistochemistry considered for assessment. Tumor stage was determined by TNM classification of malignant tumors.
Molecular Analysis
DNA was extracted from frozen tumor tissues and normal cells using the YTA kit (Yekta Tajhiz, Iran), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA concentration was measured using a Nano-Drop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Two hotspot regions in the MCR region of exon 15 were evaluated for mutations using PCR amplification and automatic DNA sequence analysis method. The primer design was based on published sequences for the genotyping procedure of mutation using genomic DNA 14. The primer sequences are shown in
Sequence Primers used for study of mutation of MCR region
| Primer sequence | TM(⁰C) | Product Length (bp) | ||
| Exon15(1) | Forward | 5'-CAAGCAGTGAGAATACGTCCACAC-3' | 61.90 | 808 |
| Reverse | 5'-AGAACCTGGACCCTCTGAACTGCA-3' | 65.42 | ||
| Exon15(2) | Forward | 5'-TCCGTTCAGAGTGAACCATGCA-3' | 62.19 | 626 |
| Reverse | 5'-AGCTGACTTGGTTTCCTTGCCA-3' | 62.68 |
Descriptive results of 57 sporadic colorectal cancer, and correlation with
| Variable | Number (%) | Rs41115AG genotype N = 35 (61.4%) | Rs41115AA genotype N = 22 (38.6%) | Pearson's rho* | P | |
| Age | ≤ 50 | 13 (22.8%) | 8 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.091 |
| > 50 | 44 (77.2%) | 27 | 17 | |||
| Sex | Male | 44 (77.2%) | 8 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.091 |
| Female | 13 (22.8%) | 27 | 17 | |||
| Stage | I | 10 (17.5%) | 7 | 3 | 0.23 | 0.056 |
| II | 11 (19.3%) | 5 | 6 | |||
| III | 6 (10.5%) | 5 | 1 | |||
| IV | 30 (52.6%) | 18 | 12 | |||
| Grade | I | 21 (36.8%) | 13 | 8 | 0.09 | 0.486 |
| II | 14 (24.6%) | 8 | 6 | |||
| III | 10 (17.5%) | 4 | 6 | |||
| IV | 12 (21.1%) | 10 | 2 | |||
| Morphological Type | Adenocarcinoma | 50 (87.7%) | 32 | 18 | 0.14 | 0.290 |
| Others | 7 (12.3%) | 3 | 4 | |||
| Subsite | Right Colon | 21 (36.8%) | 11 | 10 | 0.31 | 0.029 |
| Left Colon | 17 (29.8%) | 9 | 8 | |||
| Rectum | 19 (33.3%) | 15 | 4 | |||
| Family History of Polyps | No | 54 (94.7%) | 33 | 21 | 0.042 | 0.757 |
| Yes | 2 (3.5%) | 1 | 1 | |||
| Family History of CRC | No | 44 (77.2%) | 27 | 17 | 0.20 | 0.091 |
| Yes | 13 (22.8%) | 8 | 5 | |||
| Family History of other GI cancers | No | 42 (73.7%) | 23 | 19 | 0.23 | 0.088 |
| Yes | 15 (26.3%) | 12 | 3 |
Frequency of
| Sample | DNA change | Amino acid change | Type |
| C16 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C28 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C37 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C55 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C80 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C92 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C95 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C97 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C107 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C109 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C115 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C117 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C118 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C147 | ACG>ACA(G > A) | T1475T(Thr1475Thr) | Transition |
| C43 | 4087-4091delAAAAG | Frame shift change | |
| C109 | 4506delA | Frame shift change | |
| C110 | AGT>AGG(T>G) | SER1447ARG(S1447R) | Transversion |
Sequencing Analysis
After amplification, the purified PCR product was sequenced in both directions. The Sanger sequencing method was used for mutation detection in samples. The chromatogram files of the sequencing results were viewed and checked for quality by Finch TV1.4 software (www. geospiza.com). The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool of the NCBI webpage (BLAST; https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) was used to search for highly similar sequences available in the GenBank database retrieved from NCBI. Then, the alignment of the sample sequence with similar sequences was performed.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive data were obtained using SPSS software (version 24; IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Pearson's Chi-Square test was used to assess and report the Likelihood ratio for any correlation between defined variables (age, sex, stage, grade, morphologic type, subsite of the tumor, and positive family history) and gene pattern. For survival analysis, the outcome of interest was overall survival (OS), defined as the time of CRC diagnosis to date of death and/or last follow-up time. OS and statistical significance of survival function was assessed using the Kaplan–Meier method and the log-rank test.
Results
Descriptive analysis results
From the 60 confirmed colorectal cancers, 57 cases were eligible to enroll in the study and had enough tissue samples that were assessable to perform molecular tests. The age range was between 27-90 years old, with age mean of 63.32 (SD 15.17); 13 cases (22.8%) were ≤ 50 years old while 44 (77.2%) were over 50 years old. The most common age group was the 5th decade (n = 13, 22.8%) and 7th decade (n = 13, 22.8%). From these, 44 CRCs (77.2%) were male and 13 cases (22.8%) were female. In 21 cases (36.8%), the tumor was located in the right colon; in 17 (29.8%) the tumor was in the left colon, and in 19 cases (33.3%) the tumors were in the rectum. Most of the CRCs were adenocarcinoma (n = 50, 87.7%), and 47.4% of CRCs (n = 27) were in grade I (well-differentiated) stage of disease. From 57 CRCs, 2 cases (3.5%) had a positive family history of colorectal polyps, 13 CRCs (22.8%) had at least one relative with colorectal carcinoma, and 15 patients (26.3%) had a positive family history of other gastrointestinal system cancers. Pearson's correlation test showed that there was a significant correlation between the stage of the disease and rs41115 polymorphism (rho correlation = 0.23, P ≤ 0.05). Also, a significant correlation between anatomical subsite of tumor and rs41115 was found (rho correlation = 0.31, P ≤ 0.05). There was no significant correlation between other variables and rs41115 polymorphism.
Molecular tests results
Genomic DNA sequencing of codon 1213 to 1613 of APC gene (MCR region in exon 15) revealed a total of 4 different changes in all sporadic CRC patients (

Sequence analysis and multiple alignment results of
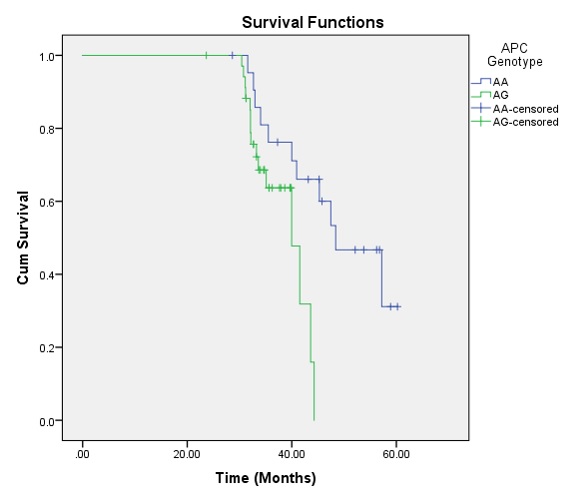
Survival function comparison between different
Survival analysis results
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed and the survival curve was created for OS function. The OS proportion was 54.4% (26 cases died). The mean OS time was 49.99 months (95% CI: 45.62 – 54.35) and the median OS was 48.40 months (95% CI: 39.04 – 57.76). Overall comparison of survival function in the different genotypes was assessed using Kaplan Meyer and Log-rank (Mantel-Cox). The tests showed that there were significant differences between groups (P Log-rank = 0.016) (Figure 2). The AG genotype had worse OS than AA genotype; mean OS time was 38.72 (95% CI: 36.61 – 40.83) for AG genotype while it was 48.81 (95% CI: 43.98 – 53.63) for AA genotype. Cox regression analysis also showed that CRCs with AG genotype had 3.24 times higher hazard of mortality than CRCs with AA genotype (HR = 3.24; 95% CI: 1.21 – 8.68, P = 0.020).
Discussion
Bi-allelic mutation of adenomatous polyposis coli () gene is an initiative process in chromosomal instability pathway of colorectal cancer pathogenesis, which leads to cancer progression, mutation, and finally gene alteration9, 17. is a tumor suppressor gene; for complete inactivation and transcription of the gene, the loss of both copies is required. gene, as a tumor suppressor gene, may be dysregulated at both somatic and germline levels in CRC pathogenesis 18. About 75% of both germline and somatic mutations are located on exon 15; this gene consists of more than 8,000 nucleotides and spans 21 exons18. However, gene somatic mutations may cause non-functional proteins, and even these small defects play an important role in colorectal cancer pathogenesis19.
We aimed to investigate common somatic mutations in exon 15 of APC genes in colorectal cancer patients in East Azerbaijan, Iran. Moreover, we sought to assess any clinicopathological aspects related to the mutation patterns and evaluate the prognostic impact of gene pattern in 57 sporadic colorectal cancers. As we did not have any background knowledge about the pattern and spectrum of the gene in our CRC population, we decided to perform a case-only study and detect the most common somatic mutations by focusing on exon 15 of the gene.
The MCR region of exon 15 was amplified and standard mutational analysis by Sanger sequencing was performed. DNA sequence data from chromatograms using the Finch TV and BLAST were analyzed. The results revealed only 4 changes, with all patients showing a nonsense mutation. As well, a missense mutation and two deletions were found. One case showed five-nucleotide deletion; however, this case did not have any different prognostic and clinicopathological aspects. Relying on the findings of only one case cannot be concluded as strong evidence of the gene mutation pattern. The overall comparison of survival function in the different genotypes of gene showed significant differences between the groups (P Log-rank = 0.016). These findings provide rationale for further comprehensive studies on the gene in CRC, particularly with a larger sample size and inclusion of other molecular techniques.
It is well-recognized that the main product of the APC gene is involved mainly in the Wnt signaling pathway and has diverse functions in this pathway beyond regulation of Wnt components18. Also, APC gene mutation mainly affects proteins in the Wnt signaling pathway, and can lead to cell division excess in a few cancers, including colorectal cancer 19. However, in CRC patients the APC mutation was reported as diverse variants 20. On the other hand, the Wnt signaling pathway is closely associated with BRAF mutation. Several studies have revealed very low incidence (0% — 3.7%) of BRAF mutation in Asian CRCs21, 22. Since we did not find any BRAF mutations in the same CRC samples as our previous study, this may evidence of the absence of any APC truncated mutation pattern 21.
The overall frequency of the gene mutation in sporadic colorectal cancer is about 25-30%, but some reports from Iran have revealed a different mutation profile 23, 24, 25, 26. This may be because of gene-environmental interaction factors and predominantly because of the heterogeneous nature of colorectal cancer. However, the gene mutation location is somehow distinct and diverse, and most commonly revealed as a frameshift mutation in exon 15 and found in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) patients. It is well-established that the nt signaling pathway is dysregulated very early in conventional adenomas by mutation of 9, 17. Although many research studies were performed on the germ-line mutation pathogenesis, especially in FAP, conclusions about mutations and/or DNA polymorphisms such as SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) pattern, as well as pathogenesis of the APC gene, have not been clear in CRC27, 28. However, a few studies have revealed that the gene may have a different performance, with a few detected SNPs in exon 15 of this tumor suppressor gene as a germline mutation19, 29, 30, 31, 32. A most recent study on common gene mutation profile in CRCs showed point mutations in exon 16 of gene with a 19.7% prevalence29, 33, 34, 35.
Although has been well-recognized as an initiator gene in colorectal cancer carcinogenesis, its prognostic role has not been well-established. Indeed, there is still a discrepancy in the impact of mutation and pattern on CRC prognosis. Few studies were performed regarding the survival status in patients with mutation. However, those results revealed that for the majority of colorectal cancer patients, inactivation of tumor suppressor gene, as one allelic mutation, did not impact the OS by itself. Only bi-allelic mutation and/or partnership with other mutations () have prognostic impact7. This has been reported from a few studies that show that CRCs with mutations in nt and pathways had significantly worse OS and poorer median survival17, 18. Siraj . revealed that mutation represents an important predictive factor in OS; however, pattern and type of gene did not have any impact on clinical outcomes in the Middle Eastern population36. Also, another report from the UK revealed that did not affect prognosis in their cohort study. However, serves as an independent prognostic variable in CRCs37. The results of our study reveal that there are significant survival function differences between the two genotypes of the gene in East Azerbaijan.
Because of limited molecular detection techniques and low sample size, we found only a 5% mutation in 57 CRCs in our study. Genome-wide association studies or epigenetic change detection methods should be performed in larger sample sizes to identify the exact molecular pathways involved in CRC in our region. We did not access the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) analysis and/or whole-genome sequencing. NGS analysis has the advantage of sequencing a few hundred genes at the hotspot regions of mentioned genes, compared with Sanger sequencing. Thus, this was the main limitation of the study herein.
Conclusion
The prognostic impact of tumor suppressor gene mutation was not well-established yet. Proper identification of the different molecular pathways in CRC pathogenesis and the different allelic variants of the responsible genes, along with assessing gene-environmental factors and their interaction, are the main key elements used to define the high-risk populations. As well, genetic susceptibility in different ethnics warrants further investigation in future studies.
Abbreviations
APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli
CIMP: CPG Island Methylator Phenotype
CIN: Chromosomal Instability
CRC: Colorectal Cancer
MCR Region: mutation cluster region
MSI: Microsatellite Instability
OS: Overall Survival
PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction
SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank to all the patients who took part in this study.
Author’s contributions
SMNG, and RD: performed the significant contributions to conceptualization and design; and the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. MHS, LV, FF: performed the drafting of the article and critical revision for important intellectual content. All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Funding
The study has been funded as a research grant, by Ministry of Health and Medical Education, Deputy of Research and Technology (Grant number: 700/98, 2015.03.14 [1394/12/24]) from Iran Ministry of Health. Also this study has been supported from Hematology and Oncology Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (ID: 60156).
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the amended Declaration of Helsinki. The institutional review board approved the study, and all participants provided written informed consent.
All patients were signed consent forms, and all personal information are confidential. The Ethics Committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, has been evaluated and confirmed this study as a Research Project. (Permit Number: IR.TBZMED.REC.1397.441).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

